
Why do metals get less reactive across a period? The most common reducing agents are metals, for they tend to lose electrons in their reactions with nonmetals. This makes it easier for the atom to give up the electron which increases its reactivity. Therefore, the attraction between the nucleus and the last electron gets weaker. The bigger the atom, the further away the last electron. Why do metals become more reactive as you move down the periodic table?Īs we go down the group, the atom gets bigger. The nucleus of the atom gains protons moving from left to right, increasing the positive charge of the nucleus and increasing the attractive force of the nucleus upon the electrons. Moving from left to right across a period, the atomic radius decreases. What happens when you travel from left to right on the periodic table?
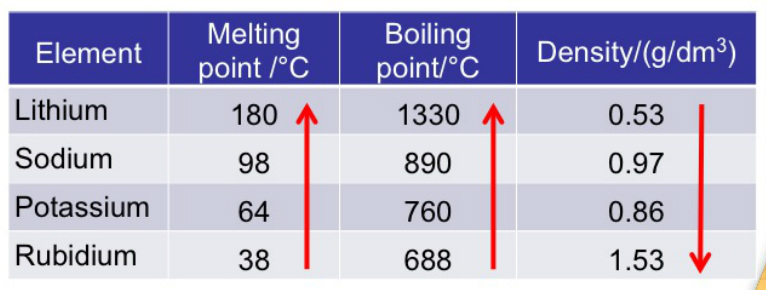
Conversely, non-metallic character generally decreases down groups and increases across a period. This arrangement reflects the periodic recurrence of similar properties as the atomic number increases.ĭoes metals increase or decrease across a period?Īcross each period, from left to right, the increasing attraction between the nuclei and the outermost electrons causes the metallic character to decrease. What happens to metals as you move across the periodic table?Įlements in the same period have the same number of electron shells moving across a period (so progressing from group to group), elements gain electrons and protons and become less metallic.

1 What happens to metals as you move across the periodic table?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
